The Essentials of System Startup: BIOS Explained & Role of RevoUninstaller

Master the Art of Force Quitting Stubborn Windows Software Instantly
How to Force Quit Windows Apps
how to force quit Windows apps ](https://store.revouninstaller.com/order/checkout.php?PRODS=28010250&QTY=1&AFFILIATE=108875&CART=1 )
There are frustrating cases when you are using an app/program on your computer and it stops responding. You try to interact with it, but nothing happens. In situations like this you will have to force quit the program on your Windows system.
When it comes to force a program to quit, there are several approaches you can take.
Force quit a program by using keyboard shortcut
If a program on your Windows system freezes or it does not respond, you can force it to quit by pressing the key combinationAlt + F4 . By pressing both keys you can force a program to quit when the program’s window is selected and active. If you pressAlt + F4 and no program windows is selected, the computers Shut Down menu will appear.
If this method does not work you can try the one below:
Force a stuck program to quit by using Windows Task Manager
This method is the most commonly used to force quit a program.
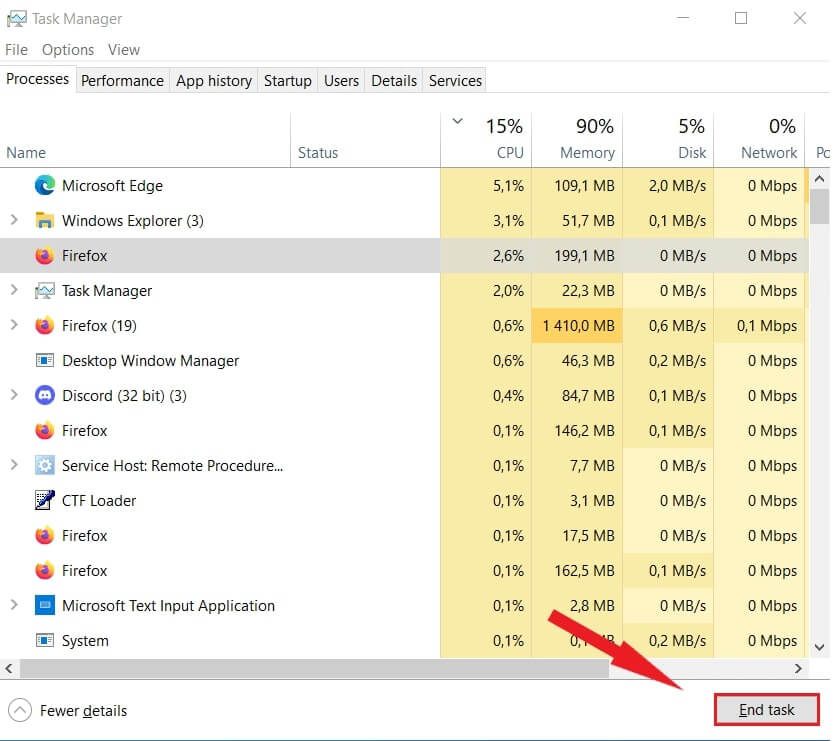
- Open the Task Manager by pressing the Win button and type in the search bar “ask Manager”. Click on the appropriate result as shown in the screenshot below.
- In some cases the Task Manager is displayed with a simple interface. To get access to the more advanced interface click the More details button on the lower left corner.
- Selec the program that is stuck. Right – click on it and select End task.

This should quit the program that is causing you issues.
Use Command Prompt to force quit a program
There are cases when Task Manager is not enough as a method to deal with a stuck program.
When this happens you need to use Command Prompt to terminate the unresponsive program. Here are the steps to follow:
- Press Win button and type
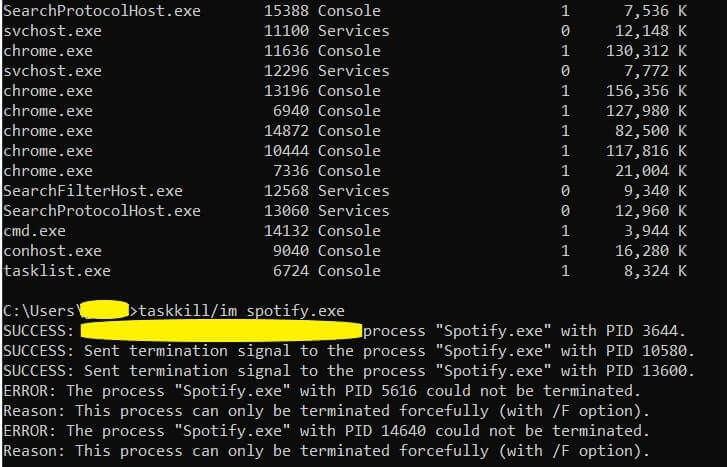
cmd - Type tasklist. This command will show you a list witl all the current running tasks and programs on your Windows computer. Find the unresponsive program’s name from the list.
- Type taskkill/im program_name.exe and press Enter.
In the example below we want to force quit Microsoft Word. I will type taskkill/im word.exe and press Enter. If you follow all the steps correctly, the command will run successfully. A message should appear that says “Sent termination signal to the process Word.exe with PID 5972”. The PID means the Proceess od which was defined by the Windows system.
![]()
We can help you every time when…
- you cannot find the program in the Apps & Features list
- the program’s built-in uninstaller is non-functional
- you have a lot of leftovers slowing down your computer’s performance
- you want to batch uninstall
- many more things
Download now
Also read:
- [New] Evaluating Storage Limits for Multi-Channel Vids, 128GB for 2024
- [New] How to Change Voice on Snapchat with 2 Easy Methods
- [New] In 2024, From Grayscale to Graded Grandeur Color Artistry
- 2024 Approved Correcting Color Misalignment in Online Videos
- 2024 Approved Top 8 YouTube Imagery Techniques for Higher Engagement
- How To Upgrade or Downgrade iPhone SE Without Data Loss? | Dr.fone
- Mastering Borderlands 3: 11 Expert Fixes for a Seamless Startup Experience
- Reversing the Clock A Complete Guide for Instagram Users
- Step-by-Step Guide to Clearing Your DNS Cache on Windows 10 & 11
- Step-by-Step Guide: Forcibly Deleting Resistant Files in Windows 11 with Revo Uninstaller
- Step-by-Step Guide: Removing a User Account on Windows 11 with Revo Uninstaller
- Step-by-Step Process for Installing Newest Driver Software in Windows 11 with Revo Uninstaller
- Tackling Total Disk Usage Overflows in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Approach
- Title: The Essentials of System Startup: BIOS Explained & Role of RevoUninstaller
- Author: Michael
- Created at : 2024-10-16 20:34:25
- Updated at : 2024-10-23 18:45:52
- Link: https://win-forum.techidaily.com/the-essentials-of-system-startup-bios-explained-and-role-of-revouninstaller/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.